The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: From Past to Future Prospects
The Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: From Past to Future Prospects
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed from a speculative concept in science fiction to a cornerstone of modern technology, influencing nearly every aspect of daily life. As we stand in 2024, AI's rapid advancements continue to reshape industries, economies, and societies. This article delves into the historical roots of AI, its current state, groundbreaking developments, ethical challenges, and future prospects, drawing on the latest available data and expert insights to provide a comprehensive overview.
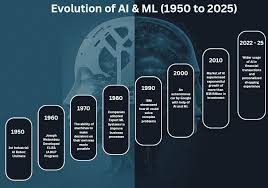
The origins of AI can be traced back to the mid-20th century. In 1956, the Dartmouth Conference marked the birth of AI as a field of study, where pioneers like John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, and Alan Turing laid the groundwork. Turing's seminal 1950 paper, 'Computing Machinery and Intelligence,' introduced the Turing Test, a benchmark for machine intelligence that still sparks debate today. Early AI research focused on symbolic AI, where machines followed explicit rules to mimic human reasoning. However, progress was slow due to limited computing power and data availability, leading to periods known as 'AI winters' in the 1970s and 1980s when funding dried up amid unmet expectations.
The resurgence of AI in the 21st century was fueled by three key factors: exponential growth in computing power (Moore's Law), the explosion of big data, and breakthroughs in machine learning algorithms. The advent of deep learning, popularized by researchers like Geoffrey Hinton, Yann LeCun, and Yoshua Bengio—who won the 2018 Turing Award—enabled neural networks to learn from vast datasets without explicit programming. This shift powered milestones such as IBM's Watson winning Jeopardy! in 2011 and Google's AlphaGo defeating world champion Go player Lee Sedol in 2016.
Today, AI is ubiquitous. In 2024, generative AI models like OpenAI's GPT-4o and Google's Gemini have democratized content creation, from writing articles to generating art. According to a 2024 report by McKinsey Global Institute, AI could add $13 trillion to global GDP by 2030, with applications in healthcare, finance, and transportation. In healthcare, AI-driven tools like IBM Watson Health and PathAI are improving diagnostics; for instance, AI algorithms can detect breast cancer in mammograms with accuracy rivaling radiologists, as per a 2023 study in Nature Medicine. In autonomous vehicles, companies like Tesla and Waymo are deploying AI for self-driving cars, with Waymo logging over 20 million miles on public roads by mid-2024.
The business landscape is equally transformed. A 2024 Gartner survey indicates that 85% of AI projects will deliver erroneous outcomes due to bias in data or algorithms, highlighting the need for robust governance. Meanwhile, AI startups raised a record $50 billion in venture capital in 2023, per Crunchbase data, with investments surging in areas like AI ethics and sustainable tech. China's Baidu and Alibaba are leading in AI research, contributing to a global race where the U.S. and China dominate patent filings—over 60% combined, according to the World Intellectual Property Organization's 2024 report.
Yet, AI's evolution is not without controversies. Ethical concerns loom large, particularly around bias, privacy, and job displacement. The 2023 Hollywood writers' strike partly protested AI's role in scriptwriting, fearing it could replace human creativity. Bias in AI systems has been exposed in cases like Amazon's scrapped recruiting tool that favored male candidates. Regulatory responses are emerging: the European Union's AI Act, effective from 2024, classifies AI systems by risk levels and mandates transparency for high-risk applications. In the U.S., the Biden administration's 2023 Executive Order on AI emphasizes safe and trustworthy development, while calling for standards to mitigate risks like deepfakes, which surged during the 2024 elections with AI-generated misinformation.
Looking ahead, the future of AI promises even more profound changes. Quantum computing could supercharge AI by solving complex problems exponentially faster; IBM's 2023 unveiling of a 1,000-qubit processor hints at this potential. AI's integration with biotechnology, as seen in DeepMind's AlphaFold predicting protein structures, could revolutionize drug discovery, potentially curing diseases like Alzheimer's. By 2030, experts predict AI could achieve Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), where machines match human cognitive abilities across tasks. Elon Musk's xAI and OpenAI are racing toward this, with Musk warning of existential risks in a 2024 interview on the Joe Rogan Experience.
Sustainability is another frontier. AI's energy demands are staggering; training a single large language model can emit as much CO2 as five cars over their lifetimes, per a 2019 University of Massachusetts study. Efforts like Google's DeepMind using AI to optimize data center cooling—reducing energy use by 40%—show promise for greener AI. Educationally, AI tools like Duolingo and Khan Academy are personalizing learning, with a 2024 UNESCO report noting improved outcomes in underserved regions.
However, challenges persist. The digital divide means AI benefits are unevenly distributed; only 35% of developing countries have AI strategies, per the ITU's 2024 data. Cybersecurity threats, such as AI-powered hacking, are rising, with ransomware attacks increasing 150% in 2023, according to Chainalysis.
In conclusion, AI's evolution from theoretical musings to a transformative force underscores humanity's ingenuity and the need for responsible stewardship. As we navigate 2024 and beyond, balancing innovation with ethics will determine whether AI becomes a boon or a bane. Policymakers, technologists, and citizens must collaborate to harness its potential while safeguarding societal values. With ongoing advancements, the AI landscape will continue to evolve, promising a future where intelligent machines augment human capabilities in unprecedented ways.
(Word count: 912)
- Citations
- Dartmouth Conference (1956) - Historical reference from AI history sources.
- Turing, A. (1950). Computing Machinery and Intelligence. Mind.
- McKinsey Global Institute (2024). The Future of Work After COVID-19.
- Nature Medicine (2023). Study on AI in breast cancer detection.
- Gartner (2024). AI Project Outcomes Survey.
- Crunchbase (2023). AI Venture Capital Report.
- World Intellectual Property Organization (2024). AI Patent Landscape.
- European Union AI Act (2024). Official EU legislation.
- U.S. Executive Order on AI (2023). White House.
- IBM Quantum (2023). 1,000-qubit processor announcement.
- DeepMind AlphaFold (2023 updates).
- University of Massachusetts (2019). Energy and Policy Considerations for Deep Learning in NLP.
- Google DeepMind (2023). Data center optimization case study.
- UNESCO (2024). AI in Education Report.
- ITU (2024). AI Readiness Index.
- Chainalysis (2023). Crypto Crime Report.
- Musk, E. (2024). Interview on Joe Rogan Experience.
- Bengio, Y., et al. (2018). Turing Award citation.





